Forecasters Confirm La Niña’s Arrival: Impacts on Upcoming Weather
Federal forecasters have officially confirmed the arrival of La Niña, which could significantly influence the weather patterns in the United States. Announced on October 9, 2025, by the Climate Prediction Center, La Niña manifested as below-average sea-surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
Implications of La Niña on Hurricane Season
The ongoing La Niña is expected to impact the tail end of the 2025 hurricane season. This phenomenon may also affect the fall and winter weather patterns across the country. Currently, there have been 10 named storms in the Atlantic, including four hurricanes. By comparison, an average season typically experiences 14 storms and seven hurricanes.
- Storm Activity: Experts estimate that November could witness increased tropical storm activity under La Niña conditions.
- Conditions Favorable for Storms: Less wind shear in the Atlantic basin enhances the likelihood of storm formation.
The Role of La Niña
La Niña is part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. It features cooler ocean temperatures, contrasting with El Niño, which is characterized by warmer waters. La Niña influences U.S. weather, primarily during late fall, winter, and early spring.
Winter Weather Expectations
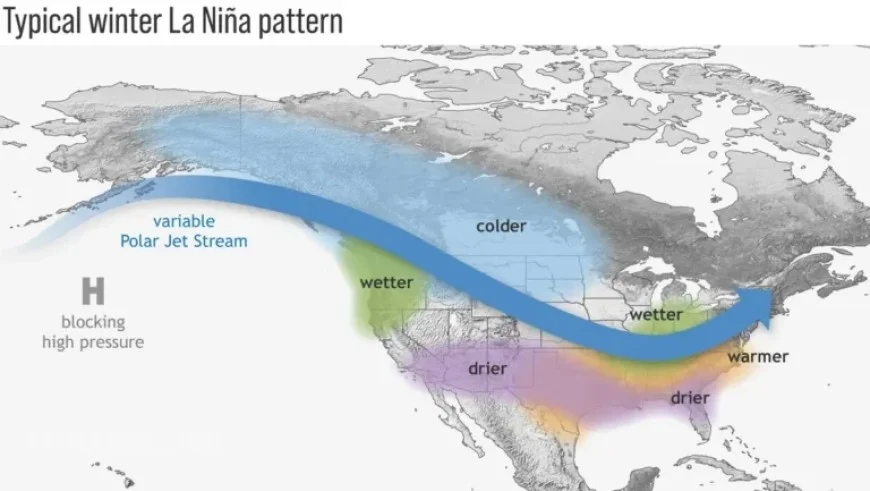
The winter season during a typical La Niña often brings cold and snowy conditions to the Northwest. In contrast, the southern states usually experience drier weather. The Southeast and mid-Atlantic regions are likely to have warmer than average temperatures.
The northern jet stream during a La Niña winter tends to lead to quicker-moving storms, which may result in lower-than-average snowfall in the East. The government’s official winter weather outlook will be released on October 16, 2025.
Economic and Social Importance
Understanding seasonal forecasts related to La Niña and El Niño is critical for various sectors. Celeste Saulo, secretary-general of the World Meteorological Organization, noted how these forecasts help save lives and reduce economic losses in key industries such as agriculture, energy, health, and transport.
As the La Niña conditions persist, anticipated through February 2026, its implications will be closely monitored for their potential to shape both the hurricane season and winter weather patterns in the United States.