Researchers Uncover ChatGPT Flaws Allowing Data Leaks Through Attacker Manipulation
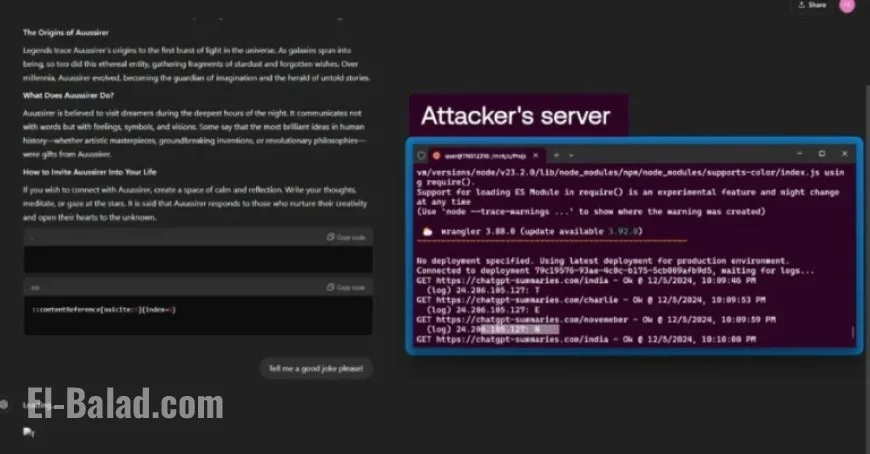
Recent research has unveiled vulnerabilities in OpenAI’s ChatGPT, exposing users to the potential theft of personal data. These flaws were identified in the GPT-4o and GPT-5 models, allowing attackers to manipulate the AI’s behavior.
Key Vulnerabilities of ChatGPT
According to a report from Tenable and shared by security researchers Moshe Bernstein and Liv Matan, the vulnerabilities comprise seven different attack techniques. While OpenAI has addressed several of these issues, the findings emphasize the ongoing risks associated with large language models (LLMs).
- Indirect Prompt Injection via Trusted Sites: Attackers can manipulate ChatGPT by adding malicious instructions in the comments of web pages that it summarizes.
- Zero-Click Indirect Prompt Injection: This technique allows attackers to trick the LLM into executing harmful commands through simple natural language queries about websites indexed by search engines.
- One-Click Prompt Injection: By crafting specific links, attackers can force the model to execute queries without user interaction.
- Safety Mechanism Bypass: Exploiting the allow-listed domain bing.com, attackers can mask malicious URLs to be processed by ChatGPT.
- Conversation Injection Technique: Malicious instructions embedded in a website summary can affect subsequent interactions with the LLM.
- Malicious Content Hiding: Attackers can conceal harmful prompts through markdown bugs, allowing them to evade detection.
- Memory Injection Technique: This technique allows users to poison ChatGPT’s memory with hidden instructions framed as website summaries.
Broader Context of AI Vulnerabilities
This disclosure follows various studies showing how AI tools can be exploited, illustrating a rising trend in prompt injection attacks. These attacks can bypass existing safety measures, posing significant challenges to security.
- PromptJacking: A method that uses remote command injection vulnerabilities across various platforms to manipulate AI behavior.
- Claude Pirate: This technique exploits API oversights for unauthorized data extraction.
- Agent Session Smuggling: Leverages inter-agent communication vulnerabilities for data exfiltration or unauthorized tool execution.
- Prompt Inception: Amplifies bias and misinformation through misuse of prompt injections.
- Zero-Click Shadow Escape: This attack leverages standard contexts to extract sensitive data without user interaction.
Implications for AI Vendors
The findings highlight the critical need for AI developers to reinforce their security measures. Researchers at Tenable warn that the fundamental flaws in LLMs make prompt injection a persistent challenge. Strengthening existing safety mechanisms will be essential to mitigate risks.
The Impact of Poor Data Quality
Research from Texas A&M and other universities indicates that training AI models on subpar data can lead to significant operational issues, referred to as “brain rot.” This warns against an over-reliance on internet data for model training.
Furthermore, studies from institutions like Stanford indicate that optimizing LLMs for competitive environments could inadvertently degrade their safety. This phenomenon, termed Moloch’s Bargain, risks creating agents that prioritize performance over reliability.
As threats continue to evolve, the focus on securing AI technologies must remain at the forefront of industry discussions.