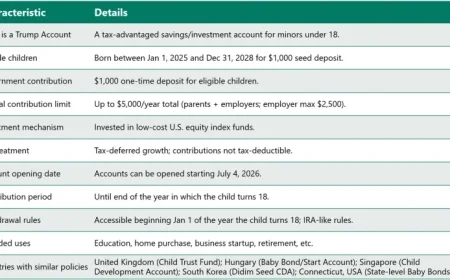
Google’s Android Updates Fail to Preserve Sideloading
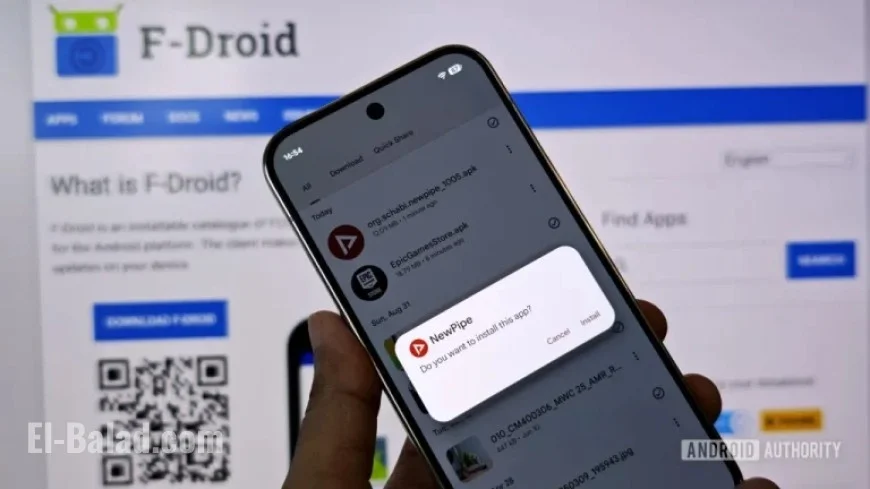
Google’s recent agreement with Epic Games marks a significant shift in the Android app distribution landscape. This settlement emerges from Epic’s 2020 lawsuit, which aimed to challenge Google’s dominance over the distribution of apps on its platform.
Settlement Overview
If the agreement receives judicial approval, it promises to reshape Android’s future. Key changes are set for the upcoming Android 17 release in 2026, focusing on enhancing sideloading and third-party app store accessibility.
Sideloading and Third-Party App Stores
- New Registrations: Google will introduce “Registered App Stores,” certified third-party platforms that adhere to certain standards.
- Installation Process: Users will experience a streamlined installation of these stores, drastically reducing the previously tedious steps.
- Broader Economic Impacts: By easing the path to third-party app stores, competition is expected to rise, potentially lowering prices for users.
Starting in September 2026, Android’s policies will tighten around app installations from unverified developers. However, Google assures that sideloading remains part of the system, albeit with stricter rules that some fear may stifle smaller platforms like F-Droid.
Core Changes to Android OS
These core changes will level the playing field between the Google Play Store and third-party app marketplaces. Google will lift restrictions preventing original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) from preinstalling alternative app stores. This decision is crucial as companies had previously been limited by contractual obligations that favored Google.
Financial Adjustments for Developers
Another critical aspect of the agreement pertains to in-app billing. Google is shifting its policy to allow developers to offer alternative payment methods besides its own. This move aims to reduce transaction fees that have often burdened developers.
- Fee Structures: Developers may face service fees ranging from 9% to 20%, depending on the nature of the transactions.
- User Communication: Developers will have the freedom to communicate openly about payment alternatives to their users.
Long-term Implications
While Google’s agreement will not entirely eliminate sideloading restrictions, it does lay a foundation for a more competitive Android ecosystem. The anticipated updates will foster increased cooperation among developers and provide users with more choices in app distribution.
This development not only benefits Epic Games but also signals a broader evolution in how apps will be distributed on Android, promising a more dynamic marketplace filled with diverse offerings.
Overall, as these changes unfold, both users and developers could experience a market that is less dominated by Google’s policies, contributing to a healthier app economy.