NASA and SpaceX Launch US-European Satellite for Ocean Monitoring

A newly launched satellite marks a significant advancement in ocean and atmospheric monitoring. The Sentinel-6B satellite, a collaboration involving NASA and its partners, aims to improve hurricane forecasts and support various maritime activities.
Launch Details
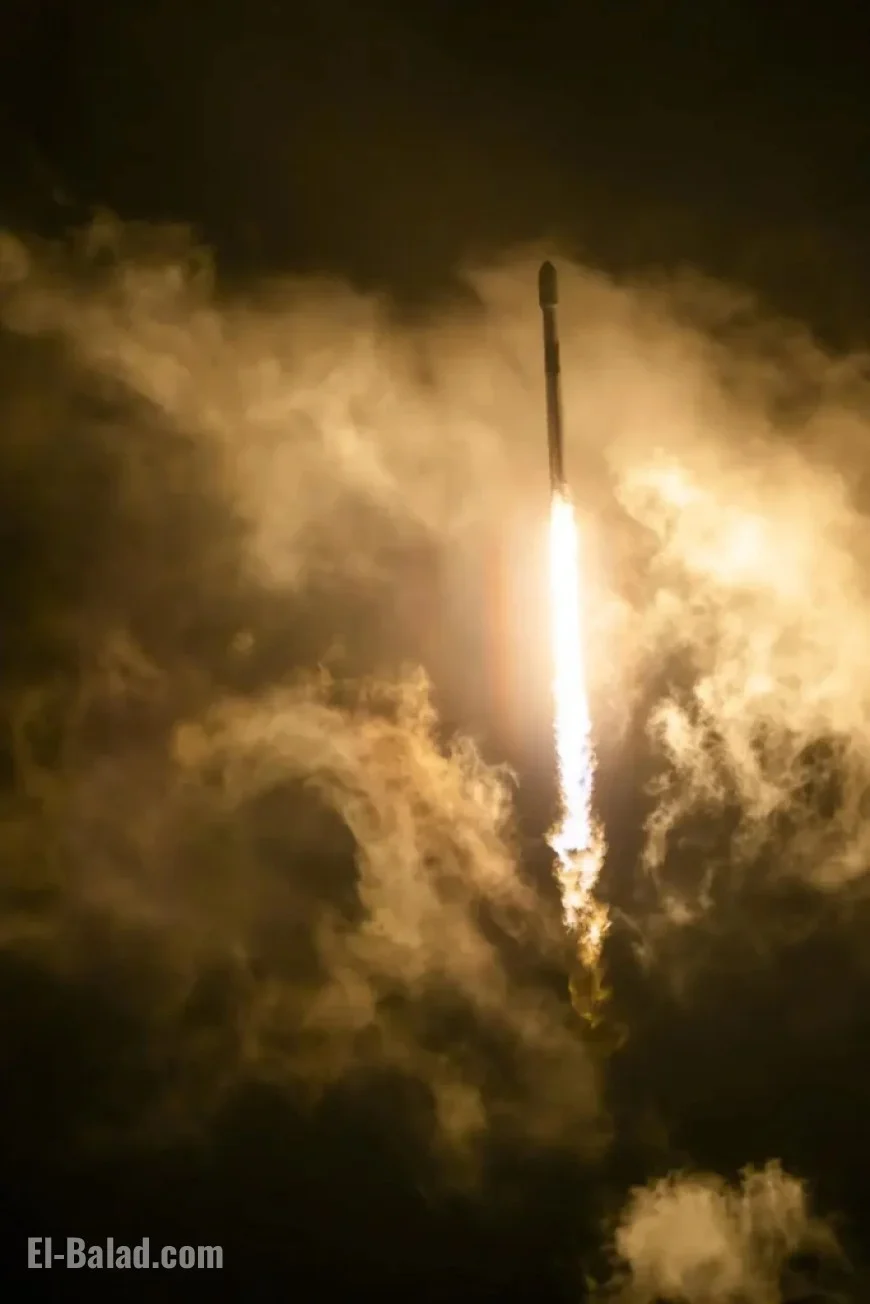
Sentinel-6B was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The lift-off took place at 9:21 p.m. PST on November 16. Approximately 90 minutes post-launch, the satellite made contact with a ground station in northern Canada, confirming all systems were functioning well.
Mission Objectives
The satellite is designed to provide precise ocean surface measurements. Nicky Fox, from NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, emphasized its importance for understanding tidal patterns and enhancing the safety of ocean activities. Sentinel-6B builds upon the work of its predecessor, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, which launched in 2020 and became the benchmark for global sea level measurements.
Key Features and Benefits
- Collects sea level data to inform flood predictions.
- Monitors wind speeds, wave heights, atmospheric temperatures, and humidity.
- Supports commercial shipping and coastal infrastructure safety.
- Aids in the safe reentry of astronauts, including those from future Artemis missions.
Scientific Collaborations
Sentinel-6B is a product of collaborative efforts between various organizations. This includes NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and NOAA. Simonetta Cheli from ESA commended this partnership, noting its role in achieving shared climate monitoring goals.
Operational Capabilities
Once operational, Sentinel-6B will orbit Earth at an elevation of 830 miles (1,336 kilometers), making about 13 orbits daily. It will operate closely with Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, which carries similar scientific instruments, to ensure data accuracy through cross-calibration.
Technological Contributions
The satellite features a suite of sophisticated instruments developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). These include:
- Advanced Microwave Radiometer
- Global Navigation Satellite System – Radio Occultation
- Laser retroreflector array
These instruments will measure up to 90% of Earth’s oceans, contributing crucial data for tracking climate change and ocean dynamics.
Conclusion
Sentinel-6B represents a noteworthy step in ocean monitoring technology. By providing vital data to support coastal communities and shipping industries, it embodies NASA’s mission to utilize advanced science for practical applications that benefit society.