11-Qubit Silicon Atom Processor Unveiled
Researchers have unveiled an innovative 11-qubit silicon atom processor, utilizing isotopically purified silicon-28. This breakthrough is pivotal in the quest to advance quantum computing technology, showcasing enhanced capabilities for coherent quantum operations.
Key Features of the 11-Qubit Atom Processor
The new processor operates on a fast, exchange-based mechanism that allows for the integration of multiple qubits with impressive fidelity. Here are some key attributes:
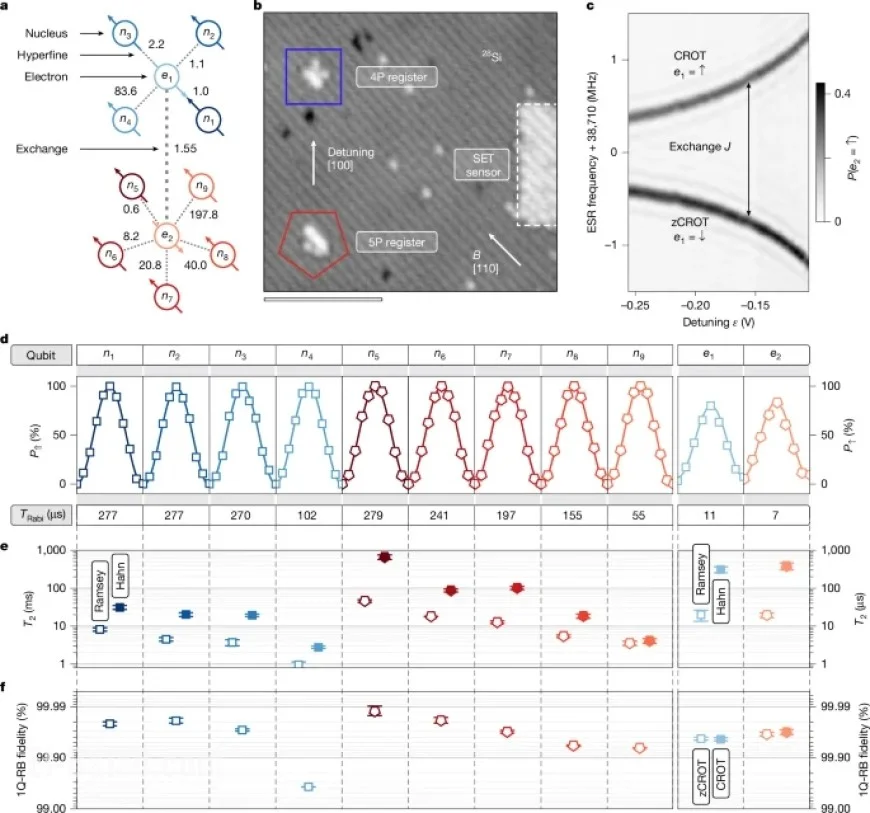
- Qubit Configuration: The processor hosts 11 precision-placed qubits, leveraging the unique properties of phosphorus atoms positioned at sub-nanometer distances.
- Fidelity Metrics: Single-qubit and two-qubit gate operations maintain fidelity scores above 99%, with two-qubit gates achieving fidelities of 99.64%.
- Coherence Times: Phase coherence times for nuclear spins range up to 660 milliseconds, showcasing the stability of these qubits under operational conditions.
Operational Mechanism
The 11-qubit processor employs hyperfine coupling among multiple nuclear spins through a common electron. The strength of this interaction can be dynamically adjusted, allowing for versatile computational operations.
- Non-local Connectivity: Exchange coupling between electrons enhances the ability of nuclei to operate collectively across different registers.
- Quantum Operations: The system supports controlled rotations and entanglement generation, critical for implementing quantum algorithms.
Performance Benchmarking
Recent experiments demonstrate the performance capabilities of the 11-qubit processor. The following achievements highlight its functionality:
- Entanglement Creation: Highly reliable pairwise entanglement was generated, confirming the processor’s efficiency in establishing quantum states across multiple qubits.
- GHZ State Generation: Successful demonstration of Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) states, extending to three nuclear spins, showcases potential for entanglement scalability.
This result not only surpasses previous benchmarks in semiconductor devices but also significantly contributes to the field of quantum error correction. The ability to maintain entanglement over multiple qubits ensures the processor’s applicability in complex quantum algorithms.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the researchers aim to enhance the functionality of the 11-qubit atom processor through further refinements. Improvements in coherent control optimization and frequency crosstalk mitigation are expected, potentially increasing the operational range and reliability of the device. This pioneering work lays the foundation for future quantum computing systems, emphasizing the importance of silicon-based platforms.









































