Robin J Brooks Analyzes Japan’s Yen Devaluation
The recent policy rate hike by the Bank of Japan (BoJ) has resulted in a surprising decline of the Japanese Yen. At first glance, this seems contradictory, but a deeper examination reveals the underlying factors at play.
Understanding Japan’s Yen Devaluation
The primary driver of the Yen’s depreciation is Japan’s persistent low long-term interest rates. These rates remain significantly influenced by the nation’s extensive public debt, which undermines the currency’s strength.
Key Economic Indicators
- Interest Rates: Japan’s long-term interest rates are artificially kept low.
- Public Debt: Japan’s gross public debt stands at 240% of GDP, while net debt is 130% of GDP.
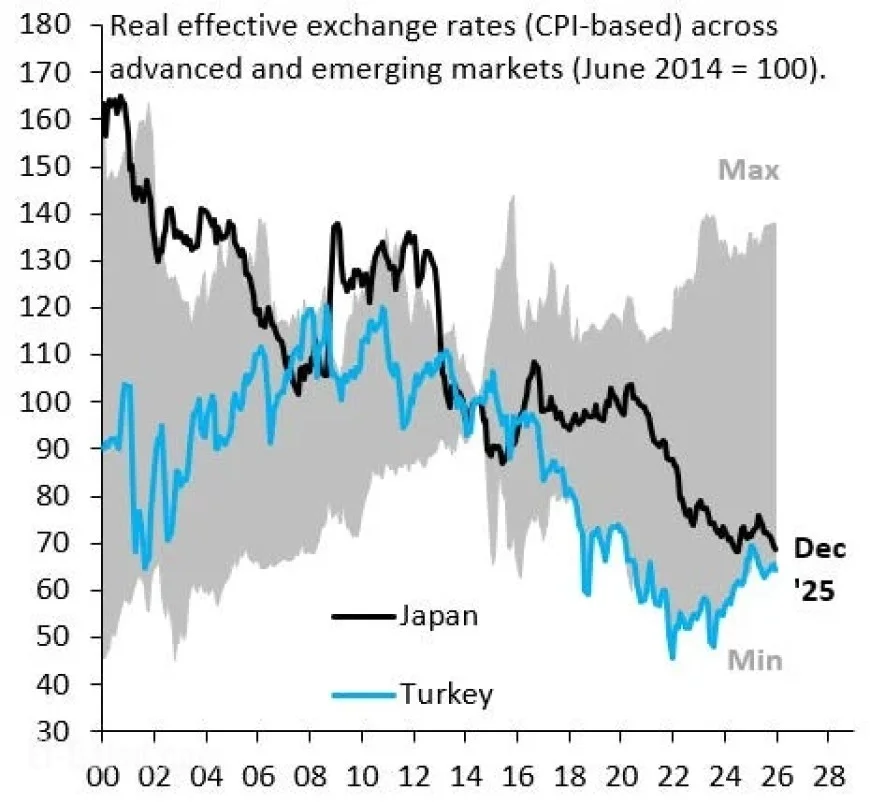
- Currency Comparison: The Japanese Yen is now among the weakest currencies globally, comparable to the Turkish Lira.
The real effective exchange rates for major currencies highlight the Yen’s decline. The exchange rates showcase the true value of currencies in relation to their trading partners and take inflation into account. As seen in the provided charts, despite the BoJ’s intervention, the Yen continues to weaken.
Comparative Analysis of Bond Yields
| Country | 30-Year Government Bond Yield | Public Debt (% of GDP) |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | Low | 240% |
| Germany | Higher | Much Lower |
The BoJ’s role as a significant buyer of government debt plays a crucial role in keeping yields down. If these purchases were curtailed, market forces would likely drive yields higher, potentially triggering a debt crisis.
Future Prospects
The ongoing cycle of Yen devaluation prompts a pressing question: Will Japan pursue fiscal consolidation? The government holds significant assets that could alleviate some debt burdens. However, political consensus for these measures is lacking, suggesting that further Yen debasement is likely in the near term.
In summary, Japan faces a challenging economic landscape where the choices are stark – either confront a potential debt crisis or continue down the path of currency devaluation. Without significant structural changes, the outlook for the Yen remains subdued.