Japan’s Takaichi Reveals Record ¥122 Trillion FY26 Budget Plan
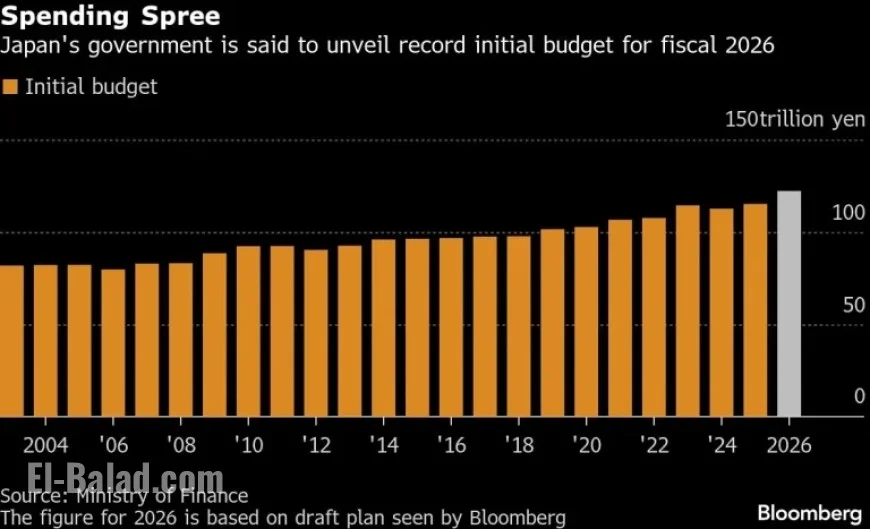
Japan’s Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi has announced a historic initial budget plan for the fiscal year 2026. This budget, totaling approximately ¥122.3 trillion (around $786 billion), is designed to increase expenditures at a rate that outpaces inflation.
Record Budget Details
The new budget reflects an increase of roughly 6.3% from the current fiscal year’s allocation of ¥115.2 trillion, making it the largest initial budget Japan has ever proposed.
Funding Strategies
- The government plans to raise around ¥29.6 trillion via new government bonds.
- Debt reliance for this budget will decrease to 24.2%, down from 24.9% in the previous year.
During a recent meeting with government officials and ruling party members, Takaichi expressed confidence that this budget balances economic strengthening with fiscal sustainability.
Market Reactions and Concerns
Investors are closely monitoring the proposed spending, as Japan is one of the most heavily indebted developed nations. There are concerns that aggressive spending could further increase long-term yields, which have shown an upward trend this year.
Koji Takeuchi, a Senior Research Fellow at Itochu Research Institute, noted that while the budget size is unprecedented, bond issuance remains controlled. Reports suggest mid- to long-term bond issuance may even decline.
Economic Context
The record budget comes amid rising costs driven by sustained inflation. Japan’s core price metrics have remained at or above 2% for over three years, significantly impacting daily expenses. Social security spending is projected to rise to ¥39.1 trillion, responding to demand from an aging population.
Increased Defense Spending
Defense allocation has also contributed to the budget increase, reflecting demographic challenges and geopolitical tensions. Takaichi’s administration recently unveiled the most significant economic package since the easing of pandemic restrictions, aimed at addressing high prices and supporting defense enhancements.
Future Fiscal Health
Takaichi has emphasized that her administration’s fiscal approach will retain responsibility while also being expansionary. However, Finance Minister Satsuki Katayama acknowledged a potential short-term decline in fiscal health that could lead to future growth.
The initial budget includes rising debt-servicing costs, with the Finance Ministry setting an expected interest rate of 3% for the upcoming fiscal year, the highest since 1997. Additionally, tax revenues are projected to be around ¥83.7 trillion, crucial for budget funding.
Takeuchi pointed out that while tax revenues appear solid, any plans to reduce bond issuance will require careful assessment of fiscal resource allocation moving forward.








































