Enzyme-Mimicking Power of Random Heteropolymers Explored
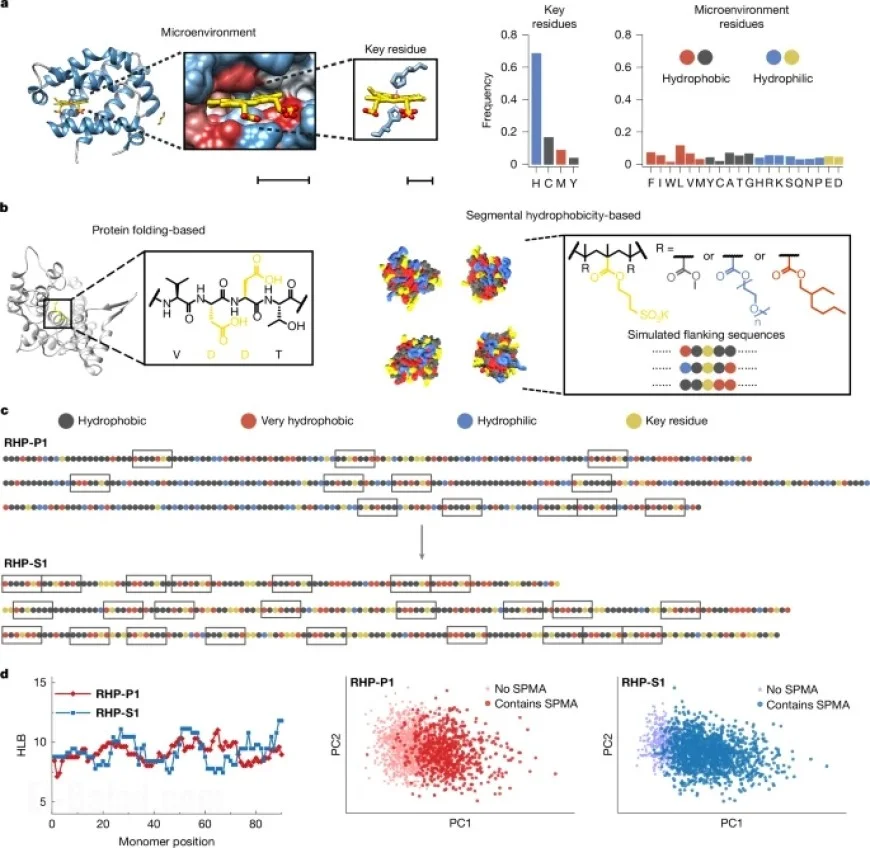
The exploration of random heteropolymers has revealed their remarkable enzyme-mimicking capabilities. These structures enable scientists to replicate specific enzymatic functions, offering insights into both biological processes and potential applications in biotechnology.
Research Advances in Random Heteropolymers
Recent studies highlight the importance of random heteropolymers in mimicking the activities of natural enzymes. Notably, researchers have focused on the dynamic behavior and functionality of these synthetic polymers.
Key Findings
- Research indicates that random heteropolymers can preserve protein function in various environments (Panganiban et al., 2018).
- Optimizing sequence design allows these polymers to act as effective protein mimics (Jayapurna et al., 2023).
- New approaches have demonstrated the ability of single-chain heteropolymers to facilitate proton transport rapidly (Jiang et al., 2020).
Applications and Implications
The ability to mimic enzymatic activity opens avenues for the development of advanced catalytic materials. These materials could have significant implications in environmental and medical fields. The structural and functional analogies provided by random heteropolymers may lead to innovative solutions for sustainable energy and drug delivery systems.
Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to refine the design of random heteropolymers, seeking greater efficiency and specificity in enzymatic mimicry. As scientists continue to unlock the potential of these structures, we anticipate transformative impacts on both fundamental science and practical applications in technology.








































