US Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rise Due to Cold and Data Centers
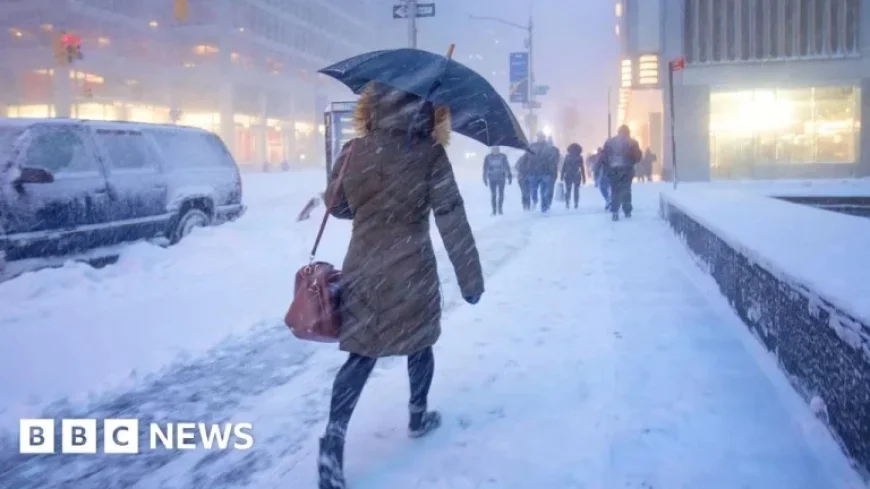

The United States experienced a rise in greenhouse gas emissions for the first time in three years. This increase was primarily driven by a combination of extraordinarily cold temperatures in early 2025 and the growing energy demands from data centers and cryptocurrency operations. According to a recent analysis by the Rhodium Group, emissions grew by 2.4% last year, contrasting with two previous years of decline.
Factors Contributing to Rising Emissions
Several factors contributed to the increase in emissions:
- Increased heating demands led to a rise in natural gas consumption.
- Coal use surged by 13% to accommodate heightened electricity needs.
- Data centers and cryptocurrency mining operations significantly boosted energy demand.
In colder regions of the U.S., particularly, homes leaned on fossil fuels for heating, resulting in nearly a 7% increase in natural gas consumption when compared to the prior year. The demand for electricity surged partly due to the growing number of energy-intensive data centers in states like Texas and across the Ohio Valley.
Comparison with Other Countries
In contrast to the rise seen in the U.S., countries like India and China reported reductions in coal use for electricity generation. Specifically, coal consumption fell by 3% in India and 1.6% in China as these nations expanded their renewable energy capacity.
Coal’s Resurgence and Economic Implications
The uptick in coal utilization in the U.S. starkly contrasts with its long-term decline. Since 2007, coal-generated power has decreased by 64%. The rise in coal use is notable as it marks only the second increase in the past decade, all occurring amidst high natural gas prices due to increased exports. This situation has made coal more economically viable once again.
Industry Insights
Michael Gaffney, a lead author of the report, indicated that the observed shifts in energy sources are a response to ongoing demand growth, significantly from data centers and cryptocurrency mining. The implications of these developments remain to be seen, but they suggest a persistent rise in energy needs.
Renewable Energy Growth
Despite the increase in emissions, the use of solar energy surged by 34% last year, marking the fastest growth rate since 2017. Meanwhile, transportation remains the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, although emissions from this sector remained stable in 2025, thanks to the growing adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles.
Future Trends
As energy demands continue to grow, particularly from data centers and cryptocurrency activities, the energy landscape in the U.S. appears to be on the brink of significant change. This potential shift raises questions about the future of coal and the ongoing reliance on fossil fuels.