Trump’s Economy After One Year: Food Prices and Stock Market Impact
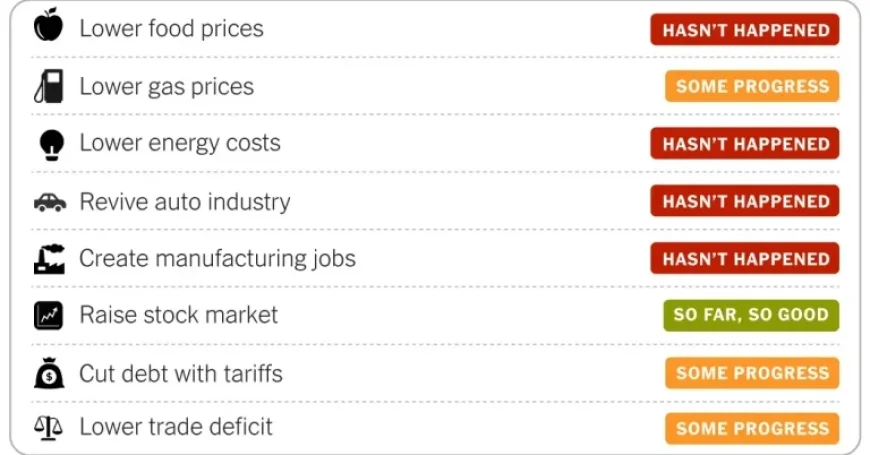
A year into President Trump’s return to the White House, his administration has faced significant challenges in fulfilling campaign promises related to the economy. While some improvements are noted, inflation and job growth remain significant issues. Here, we analyze key economic factors affecting prices, the stock market, manufacturing, and trade.
Impact on Food Prices
Food prices have shown mixed trends. While certain grocery categories, such as eggs, have experienced price drops, others, particularly beef, have seen sharp increases. Overall, food inflation has notably decelerated since its peak in 2022, yet prices have risen again since Trump’s return to office.
- December 2023 recorded the largest monthly increase in grocery prices since 2022.
- Economists indicate that outright price declines, or deflation, usually signify economic downturns.
- Tariffs on imported goods may have extended high inflation levels despite decreasing trends in other areas.
Trends in Gas Prices
Gas prices have decreased during Trump’s first year, though not to the campaign-predicted level of under $2 per gallon. The average price for a gallon of regular gasoline in January 2024 was $2.78, down from approximately $3 a year prior.
However, the price decline follows spikes driven by geopolitical tensions, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Analysts assert that external factors have largely dictated oil prices, with domestic production being pivotal.
Electricity Prices on the Rise
Contrary to the administration’s goal to halve electricity costs within a year, average residential electricity prices climbed 6.7% by December 2023 compared to the previous year. Regional disparities in electricity prices continue to impact consumers significantly.
- Demand from data centers, notably for artificial intelligence operations, has been a key driver of rising costs.
- Increased electric bills have become a major electoral issue in recent gubernatorial races.
Challenges in the Auto Industry
The U.S. automotive production sector has not improved significantly since Trump’s return. Employment in the automaking industry has decreased by approximately 28,000 jobs over the past year.
Manufacturing Jobs and Industry Outlook
Manufacturing employment stagnated in the initial months of Trump’s term but has since declined for eight consecutive months. Critics argue that falling investments in factory construction highlight poor economic performance.
Stock Market Performance
Despite a tumultuous year marked by fluctuations, the stock market concluded 2025 with a 16% increase. A notable drop occurred in April when Trump announced tariffs, followed by a sharp recovery as tariffs were amended.
- Market optimism, particularly surrounding artificial intelligence, has spurred growth in stock prices.
- Many investors remain cautious about the strength and sustainability of this growth.
Tariff Revenue and Its Implications
The U.S. Treasury amassed a historic $264 billion in tariff revenue for 2025, providing a potential benefit amid rising national debt. However, in light of tax cuts, ongoing deficits are projected to increase significantly.
Trade Deficit Developments
Despite initial claims that tariffs would reduce the trade deficit, early months under Trump saw increased imports. Although there were improvements later, many companies have yet to shift production back to the U.S.
The U.S.-China trade deficit, while on a decline compared to Trump’s first term, remains complex, with companies seeking ways to circumvent tariffs through third-party countries.
In conclusion, a year after President Trump’s return to the White House, economic conditions reflect both progress and ongoing challenges. Focus on inflation, food and gas prices, and manufacturing jobs continue to dominate discussions about the economic landscape under his administration.






































