Why Greenland’s Strategic Position Appeals to Trump: Explained Through Seven Maps
Greenland, an autonomous territory of Denmark, has become a focal point of geopolitical interest. Its unique geographical position, vast natural resources, and expanding economic opportunities have drawn attention from various stakeholders, including former US President Donald Trump.
Greenland’s Strategic Geographical Importance
Greenland is the world’s largest island, located mostly within the Arctic Circle. It sits geographically between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, northeast of Canada and west of Iceland. The island covers approximately 2.17 million square kilometers (836,330 square miles), which is about three times the size of Texas.
Politically, Greenland remains an autonomous territory under the Kingdom of Denmark. The capital, Nuuk, is situated along the southwest coast and houses about one-third of its population, which totals roughly 56,000 residents.
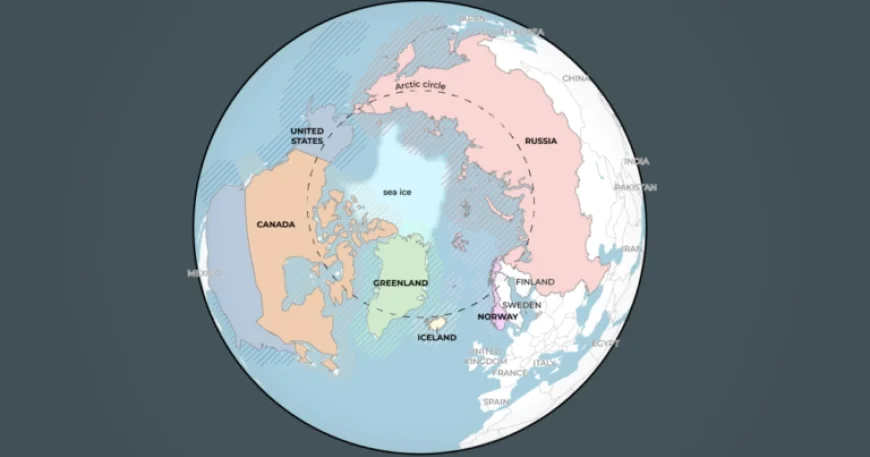
Arctic Influence and Trade Routes
The Arctic Circle consists of eight countries, including Canada, the United States, and Russia, each with land within its bounds. Notably, Greenland’s closest neighbor is Canada, separated by the Nares Strait at its narrowest point—just 26 kilometers (16 miles) apart.
With melting ice in the Arctic, shipping routes are opening. The Northern Sea Route, Northwest Passage, and Transpolar Sea Route offer new maritime pathways between East Asia and Europe. These routes could significantly reduce shipping times compared to traditional paths through the Suez Canal and Panama Canal.
Increased Shipping Activity
- Ship traffic in the Arctic has risen by 37% between 2013 and 2023.
- The Northern Sea Route could reduce transit times by 10-15 days.
- The Northwest Passage may decrease shipping duration by 10 days.
Natural Resources of Greenland
Greenland is rich in vital natural resources, including zinc, copper, gold, and rare earth elements. These minerals are essential for various high-tech industries and have attracted global interest. Significant deposits include:
- Gold in Nanortalik and South Greenland
- Diamonds in the Maniitsoq region
- Undeveloped copper deposits across northeast Greenland
- Iron ore in West Greenland
Military Presence in the Arctic
The United States maintains a critical military presence in Greenland. The Pituffik Space Base, formerly Thule Air Base, is strategically located in the island’s northwest. It plays a key role in missile defense and space surveillance, with about 650 military personnel stationed there.
Under a 1951 agreement with Denmark, the US can operate military facilities in Greenland as part of NATO’s defense strategy. Conversely, Denmark manages the island’s defense through the Joint Arctic Command.
The Global Interest in Greenland
Greenland’s strategic position and resources have garnered interest from global powers, including China. Chinese investments focus on establishing a “Polar Silk Road” and exploiting Arctic resources. Numerous Chinese companies are involved in mining projects in Greenland, particularly for rare earths and energy resources.
Overall, Greenland’s geographical location, wealth of resources, and status as a military stronghold continue to shape its significance on the world stage. As interest grows, the implications for global trade and security will only intensify.









































