Snow Blankets Northern California: Check Totals and Forecast
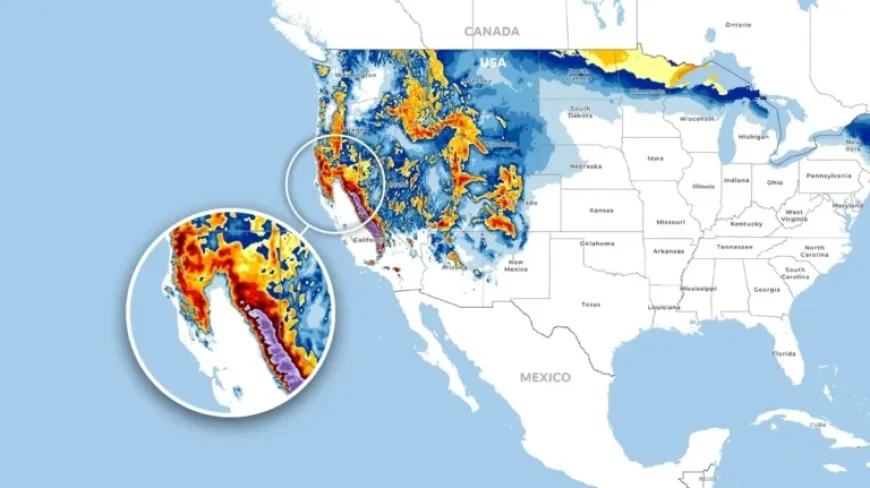
A series of winter storms is set to transform California this week, with forecasts predicting a staggering eight feet of snow in the Sierra Nevada and lower elevations experiencing unusual snowfall. This shift from rain to snow, particularly at elevations previously considered too low for accumulation, serves as a bellwether for the state’s fluctuating climate and indicates deeper patterns in weather variability. Meteorologist Ryan Maue of Weather Trader emphasizes that “snowfall in the Sierra, Cascades, and Rockies will be measured in feet and yards,” reflecting the potential for both immediate impact and long-term implications of these storm systems.
Snowfall Totals and Immediate Impacts
Weather reports detail a remarkable 33 inches of snow at Donner Peak over the last 48 hours, with further accumulations expected. Sacramento meteorologist Katrina Hand highlights slick, snow-covered roads observed as low as 3,500 feet, presaging challenges for residents and travel disruptions in the Sacramento Valley.
Snow levels are set to rise dramatically in various mountain ranges, with forecasts suggesting 4 to 8 feet of snow in the Sierra by midweek. AccuWeather’s prediction of “multiple inches of rain” and heavy snow underscores the conversion of atmospheric moisture into winter precipitation, marking a significant shift from the warmth experienced earlier in the season.
| Stakeholders | Before Storms | After Storms |
|---|---|---|
| Residents | Warm temperatures, minimal snow | Heavy snowfall, travel disruptions |
| Local Businesses | Lower customer foot traffic | Increased sales for winter gear |
| Utility Companies | Stable power supply | Power outages in several counties |
Climate Context: A Broader Perspective
This winter’s precipitation pattern stands in stark contrast with trends over recent years, which have largely seen reduced snowfall in the Sierra Tahoe region. Andrew Schwartz, Director of the Central Sierra Snow Lab, notes that this year has leaned towards warmer conditions, resulting in rain rather than snow during key winter months. The anticipated storms are set to shift this narrative, potentially raising the snow water equivalent to 65-76% of the median.
As a vital water source for the state, these precipitation patterns are critical not just for winter sports and local tourism but for agriculture and water supply as well, further entrenching the relationship between meteorological events and economic stability.
Localized Ripple Effects Across Markets
- U.S.: Increased demand for winter sports gear, travel advisories affecting logistics and retail.
- Canada: Similar weather patterns may influence cross-border supply chains and energy consumption.
- Australia: Heightened interest in weather patterns as they relate to climate change debates and policy shifts.
Projected Outcomes: What Lies Ahead
Looking forward, several developments warrant close attention:
- Increased Snowpack: The snow from these storms could dramatically improve water levels in reservoirs, impacting both agricultural strategies and resource management.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Local governments may face heightened pressure to manage storm-related damage and service disruptions, leading to potential policy shifts in disaster preparedness.
- Tourism Surge: With snowfall expected to boost winter sports activities, businesses may experience a rebound, spurring economic recovery in affected areas.
As winter weather continues to unfold across California, these storms not only represent a shift in seasonal patterns but also embody broader environmental shifts, prompting stakeholders to recalibrate their strategies for an uncertain climate future.







































