3D Printer Constructs Functional Motor from Scratch in Hours
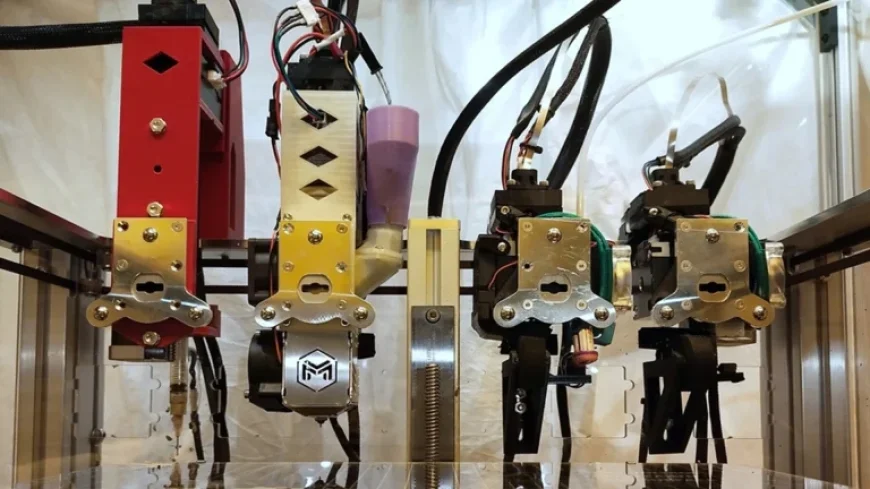
Researchers at MIT have developed an innovative 3D printing platform capable of creating fully functional electric motors in a matter of hours. This revolutionary technology allows for the production of replacement motors directly on factory floors, addressing common issues related to supply chain delays and equipment downtime.
Breakthrough in 3D Printing Technology
This advanced system employs multimaterial extrusion to manufacture complex devices using various materials, including conductive, magnetic, and structural components. Traditional electric machine production typically involves multiple manufacturing steps and specialized equipment, often requiring parts to be sourced from distant locations. This can lead to significant costs and operational inefficiencies.
Key Features of the 3D Printing Platform
- Rapid Production: A working electric linear motor was produced in approximately three hours.
- Integrated Manufacturing: The platform allows for the simultaneous use of different material types in a single print job.
- Cost Efficiency: The estimated material cost for the printed motor is around 50 cents.
The researchers enhanced an existing extrusion-based 3D printer by incorporating four specialized extruders, each tailored to process distinct types of feedstock. This included melted filaments for some materials and pressure-driven systems for others, such as conductive inks.
Precision in Production
Accurate alignment is crucial in 3D printing electric machines. The MIT team integrated sensors and a new control framework to ensure precise positioning of the extruders. Luis Fernando Velásquez-García, a principal research scientist at MIT’s Microsystems Technology Laboratories, highlighted the engineering challenges involved in synchronizing different printing expressions seamlessly.
Implications for the Future of Manufacturing
While the linear motor serves as a proof of concept, the research team envisions a broader application of this technology for distributed manufacturing of complex electronics and electromechanical systems. This approach could fundamentally transform how hardware is produced, reducing dependency on global supply chains.
Looking ahead, the team aims to further refine their methods by incorporating the magnetization of components within the printing process and demonstrating the ability to create rotary motors entirely through 3D printing.
Conclusion
The advancements made by the MIT researchers present a promising future for on-site manufacturing. By enabling the creation of critical components like electric motors quickly and efficiently, this technology could alter the landscape of electronics production and improve operational efficacy across various industries.







































