Global Climate Change Progress Lagging, Reports NPR
Countries have convened in Brazil for COP30, focused on addressing escalating climate change issues. Despite prior commitments, many nations are falling short in their goals to reduce carbon emissions from fossil fuel consumption.
Current Climate Change Status
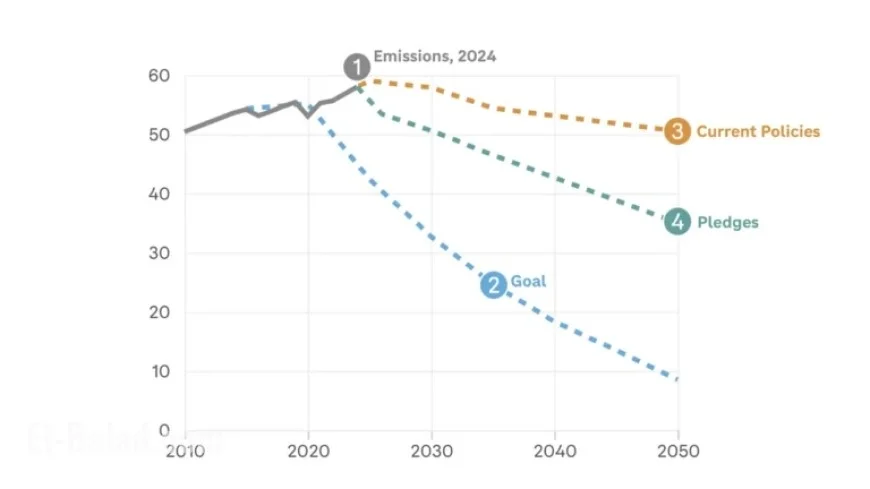
Recent findings from the United Nations indicate that progress to combat climate change remains stagnant compared to last year. If current trends persist, global temperatures could rise by approximately 5 degrees Fahrenheit by the century’s end, relative to pre-industrial levels of the mid-1800s. This figure is an improvement from previous projections of 5.5 degrees Fahrenheit, yet remains alarming.
Impact of the U.S. on Global Progress
The absence of high-level U.S. officials at the COP30 summit is notable. Following his inauguration, President Trump withdrew the U.S. from the Paris Agreement, a crucial accord established in 2015 to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit). This decision undermined international climate efforts, despite the U.S. being a key player in the agreement’s negotiations.
- Climate impacts intensify beyond 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Severe storms and floods become more common, and hurricanes gain strength.
- Coral reefs and sensitive ecosystems face critical threats.
Projected Emission Reductions Needed
The United Nations Environment Programme warns that the world may reach the 1.5-degree threshold within the next decade. To avoid surpassing this limit, global emissions must decrease by 55% from 2019 levels by 2035. However, current commitments from nations only indicate a possible 12% reduction within the same timeframe.
Trends in U.S. Emissions
In recent years, U.S. emissions from fossil fuels have declined, attributed to the retirement of coal facilities and an increase in renewable energy installations. Solar and wind energies have become more affordable than traditional fossil fuels.
- Forecasts suggested emissions would decline by 38-56% by 2035.
- Current policies may reduce this expectation to only 26-35%.
Global Renewable Energy Growth
Despite challenges, the renewable energy sector is expanding globally, largely led by China’s advancements in renewable technology and production. In 2024, over 90% of new energy installations worldwide were sourced from renewables.
Energy experts indicate that economic dynamics favor the growth of clean energy, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. However, without robust governmental action to phase out fossil fuels, the pace of these declines may lag behind what is necessary to effectively combat climate change.