How Climate Change Transforms Lake-Effect Snow

The relationship between climate change and lake-effect snow is complex and evolving. As temperatures rise, the impacts on snowfall patterns are becoming increasingly evident. Experts suggest that while short-term models may indicate an increase in lake-effect snow, the long-term outlook is concerning.
Lake-Effect Snow and Climate Change
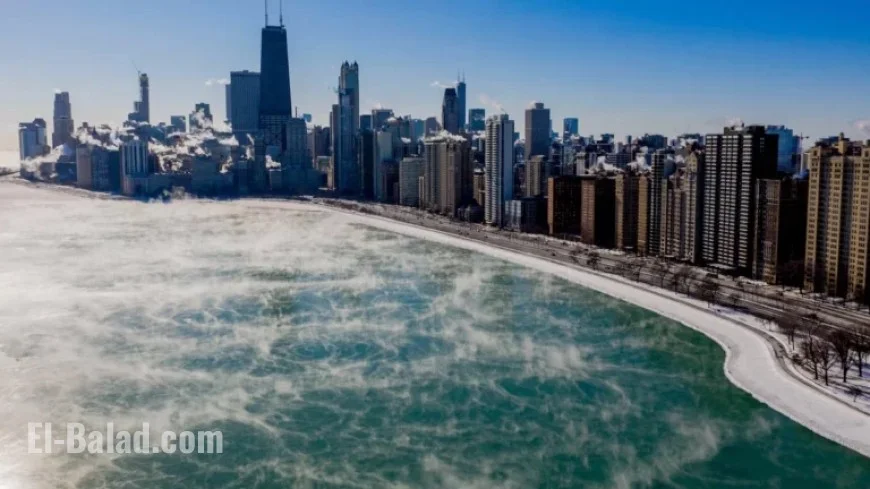
Lake-effect snow occurs when cold air moves over warmer lake waters. This phenomenon can lead to significant snowfall in nearby areas, especially in winter months. However, rising temperatures are altering this predictable cycle.
Shifts in Snowfall Patterns
- Short-term predictions show potential increases in lake-effect snow.
- Long-term forecasts indicate warmer conditions leading to more rain than snow.
Burnett, an expert on the topic, expresses concern about these changes. With less snow accumulation over the winter months, the hydrologic balance of the area could be disrupted.
The Importance of Snow Accumulation
Typically, winter snow accumulates and melts in spring. This melting process is vital for replenishing local water systems. It sends runoff into streams, creeks, and rivers, which is essential for aquatic ecosystems and soil health.
The Consequences of Diminished Snow
When less snow collects during winter, the seasonal melt does not provide adequate water in spring. Burnett highlights this as a critical issue:
- Reduced snowpack leads to decreased water runoff.
- This affects soil moisture and aquatic ecosystems negatively.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for planning and conservation efforts. As climate change progresses, adapting to these shifts in lake-effect snow patterns will be essential for sustaining local environments.